Registered User mNo edit summary |
Registered User mNo edit summary Tag: 2017 source edit |
||
| (One intermediate revision by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 63: | Line 63: | ||
|} | |} | ||
<noinclude> | |||
[[Category:Getting started with STM32|14]] | |||
{{PublicationRequestId | 16100 | 13.05.2020 | Philippe SAGE}} | {{PublicationRequestId | 16100 | 13.05.2020 | Philippe SAGE}} | ||
{{ArticleBasedOnModel | Example STM32 Step by step article}} | {{ArticleBasedOnModel | Example STM32 Step by step article}} | ||
</noinclude> | </noinclude> | ||
Latest revision as of 16:24, 27 May 2024
Build an IOT system![]() 30min
30min
Target description
This tutorial shows how to program and use the Bluetooth interface to perform data communication between the STM32L4 Discovery kit IoT node (B-L475E-IOT01A) and an Android application running on a mobile device.
After this tutorial, you will be able to build an IoT system, control it from your mobile monitoring sensors and collect data.
Prerequisites
You have gone through:
Hardware
- STM32L4 Discovery kit IoT node[1] (B-L475E-IOT01A )
- USB cable Type-A to Mini-B
Literature
- UM2153 Discovery kit for IoT node, multi-channel communication with STM32L4
- UM1873 Getting started with the X-CUBE-BLE1 Bluetooth® Low Energy software expansion for STM32Cube4
 Getting starting with STM32L4 Discovery kit IoT node
Getting starting with STM32L4 Discovery kit IoT node
The purpose of this section is to explain step-by-step how to reuse one of the applications that are part of the STM32CubeL4 MCU package to create a communication channel between the IoT board emulating a heart rate monitor and a mobile device on which the data is displayed via an Android application.
1. Import and convert the HeartRate project from the STM32Cube package
- In STM32CubeIDE, import the HeartRate example located in: C:\Users\user_name\STM32Cube\Repository\STM32Cube_FW_L4_Vx.xx.x\Projects\B-L475E-IOT01A\Applications\BLE\HeartRate
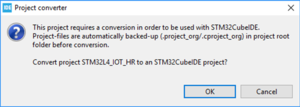
- The project must be converted and the following message is displayed:
- Click on OK and a new message confirms the success of the conversion
- Click on OK and the STM32CubeIDE workspace opens
2. Build and execute the HeartRate Project
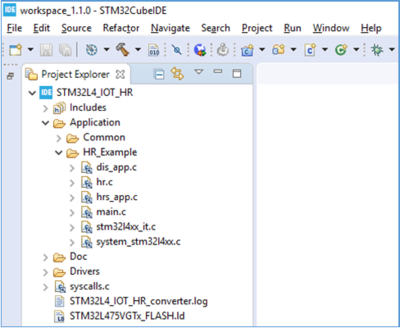
- Select the STM32L4_IOT_HR project
- Click on the Build button
 to rebuild the project.
to rebuild the project. - Click on the Debug button
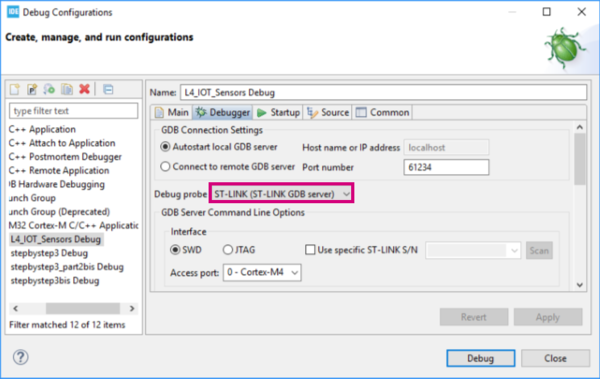
 arrow and select Debug Configurations… and make sure the Debug probe parameter is set to ST-LINK. Otherwise the code is not properly downloaded on the board.
arrow and select Debug Configurations… and make sure the Debug probe parameter is set to ST-LINK. Otherwise the code is not properly downloaded on the board.
- Click on the Debug button
 to run the software.
to run the software. - STM32CubeIDE opens the Debug perspective. Click on the Resume button
 to execute the code.
to execute the code.
3. Install the Android application on a mobile device
To interact with the IoT board, an Android application has to be installed on a mobile device.
The STM32 BLE Profile application is a companion tool to show in a human readable form all notifications coming from Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE) devices implementing some peripheral profiles.

4. Connect to the IoT node
- Go to Google Play store and install the “STM32 BLE Profiles” application on your mobile device.
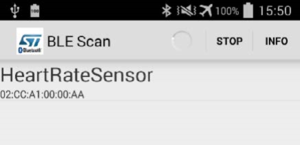
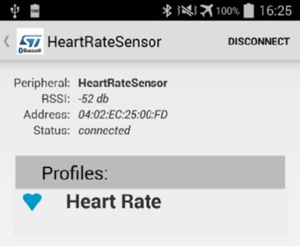
- Once installed, simply launch the STM32 BLE Profiles application. The application scans the network and displays a list of discovered BLE devices (Here the HeartRateSensor device).
- Establish a Bluetooth connection with the B-L475E-IOT1A board selecting the HR_L475_IoT device from the discovered devices list. It can take a while to get the connection established.
- The following screenshot shows the successful pairing with a health thermometer sensor:
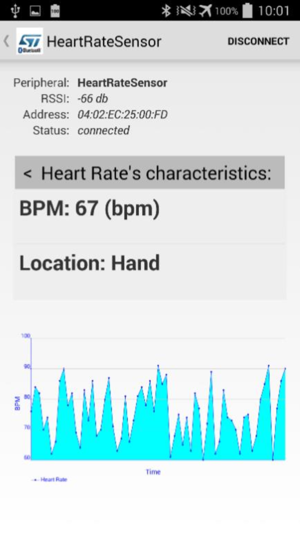
- Once connected, select the Heart Rate profile among the BLE profiles proposed.
The application starts to display the heart rate data sent by the IoT connected device, which acts as a peripheral. In this example, the data is generated on the B-L475E-IOT1A board via a formula and does not reflect the data from a real sensor.
Now you are able to:
- Build your own IoT system to get values from a peripheral device and display them on your mobile device
- Regenerate a project from one of the various applications available in the STM32Cube package.
5. References