Registered User mNo edit summary |
Registered User Tag: 2017 source edit |
||
| (29 intermediate revisions by 7 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{ApplicableFor | |||
|MPUs list=STM32MP13x, STM32MP15x, STM32MP21x, STM32MP23x, STM32MP25x | |||
|MPUs checklist=STM32MP13x, STM32MP15x, STM32MP21x, STM32MP23x, STM32MP25x | |||
}} | |||
<noinclude></noinclude> | |||
==Linux configuration genericity== | ==Linux configuration genericity== | ||
The process of building a kernel has two parts: configuring the kernel options and building the source with those options. | The process of building a kernel has two parts: configuring the kernel options and building the source with those options. | ||
| Line 8: | Line 13: | ||
For OpenSTLinux distribution the defconfig is located into the kernel source code and fragments into stm32mp BSP layer : | For OpenSTLinux distribution the defconfig is located into the kernel source code and fragments into stm32mp BSP layer : | ||
:- arch/arm/configs/'''multi_v7_defconfig''' | :- arch/arm/configs/'''multi_v7_defconfig''' for arm 32bits | ||
Every new kernel version brings a bunch of new options, we do not want to back port them into a specific defconfig file each time the kernel releases, so we use the same defconfig file based on ARM SoC | :- arch/arm64/configs/'''defconfig''' for arm 64bits | ||
Every new kernel version brings a bunch of new options, we do not want to back port them into a specific defconfig file each time the kernel releases, so we use the same defconfig file based on ARM SoC architecture.<br> | |||
STM32MP specificities are managed with fragments config files. | |||
:- meta-st/meta-st-stm32mp/recipes-kernel/linux/linux-stm32mp/<kernel version>/'''fragment-*.config''' | :- meta-st/meta-st-stm32mp/recipes-kernel/linux/linux-stm32mp/<kernel version>/'''fragment-*.config''' | ||
.config result is located in the build folder: | |||
.config | :- build-openstlinuxweston-<machine name>/tmp-glibc/work/<machine>-ostl-linux-gnueabi/linux-stm32mp/<kernel recipe version>/build/'''.config''' | ||
:- build-openstlinuxweston- | or config-<kernel-version> result is located in the deploy folder: | ||
:- build-openstlinuxweston-<machine name>/tmp-glibc/deploy/image/<machine name>/kernel/'''config-<kernel recipe version>''' | |||
{{Highlight|To modify the kernel options, it is not recommended to edit this file directly.}} | {{Highlight|To modify the kernel options, it is not recommended to edit this file directly.}} | ||
* A user runs either a text-mode : | * A user runs either a text-mode : | ||
{{PC$}} make config | {{PC$}}make config | ||
starts a character based question and answer session (Figure 1) | starts a character based question and answer session (Figure 1) | ||
[[File: Make_config.png|thumb|upright=4|left|link=|Figure 1. Configuring the kernel with make config]]<br clear=all> | [[File: Make_config.png|thumb|upright=4|left|link=|Figure 1. Configuring the kernel with make config]]<br clear=all> | ||
{{PC$}} make menuconfig | {{PC$}}make menuconfig | ||
starts a terminal-oriented configuration tool (using ncurses) (Figure 2) | starts a terminal-oriented configuration tool (using ncurses) (Figure 2) | ||
The ncurses text version is more popular and is run with the make menuconfig option. | The ncurses text version is more popular and is run with the make menuconfig option. | ||
| Line 33: | Line 42: | ||
* or a graphical kernel configurator : | * or a graphical kernel configurator : | ||
{{PC$}} make xconfig | {{PC$}}make xconfig | ||
starts a X based configuration tool (Figure 3) | starts a X based configuration tool (Figure 3) | ||
| Line 54: | Line 63: | ||
For this use case, the prerequesite is that OpenSTLinux SDK has been installed and configured. | For this use case, the prerequesite is that OpenSTLinux SDK has been installed and configured. | ||
To verify if your cross-compilation environment has been put in place correctly, run the following command: | To verify if your cross-compilation environment has been put in place correctly, run the following command:<br/> | ||
{{PC$}} set | grep CROSS | For Arm32bits: | ||
'''Arm32bits''' {{PC$}}set | grep CROSS | |||
CROSS_COMPILE=arm-ostl-linux-gnueabi- | CROSS_COMPILE=arm-ostl-linux-gnueabi- | ||
For Arm64bits: | |||
'''Arm64bits''' {{PC$}}set | grep CROSS | |||
CROSS_COMPILE=aarch64-ostl-linux- | |||
For more details, refer to ''<Linux kernel installation directory>/README.HOW_TO.txt'' helper file (the latest version of this helper file is also available in GitHub: {{CodeSource | meta-st-stm32mp | recipes-kernel/linux/linux-stm32mp/README.HOW_TO.txt | README.HOW_TO.txt}}). | For more details, refer to ''<Linux kernel installation directory>/README.HOW_TO.txt'' helper file (the latest version of this helper file is also available in GitHub: {{CodeSource | meta-st-stm32mp | recipes-kernel/linux/linux-stm32mp/README.HOW_TO.txt | README.HOW_TO.txt}}). | ||
* Go to the <Linux kernel build directory> | * Go to the <Linux kernel build directory> | ||
{{PC$}} cd <Linux kernel build directory> | {{PC$}}cd <Linux kernel build directory> | ||
* Save initial configuration (to identify later configuration updates) | * Save initial configuration (to identify later configuration updates) | ||
{{PC$}} make | '''Arm32bits''' {{PC$}}make ARCH=arm savedefconfig | ||
'''Arm64bits''' {{PC$}}make ARCH=arm64 savedefconfig | |||
Result is stored in defconfig file | Result is stored in defconfig file | ||
{{PC$}} cp defconfig defconfig.old | {{PC$}}cp defconfig defconfig.old | ||
* Start the Linux kernel configuration menu | * Start the Linux kernel configuration menu | ||
{{PC$}} make | '''Arm32bits''' {{PC$}}make ARCH=arm menuconfig | ||
'''Arm64bits''' {{PC$}}make ARCH=arm64 menuconfig | |||
* Navigate forwards or backwards directly between feature | * Navigate forwards or backwards directly between feature | ||
| Line 81: | Line 96: | ||
* Compare the old and new config files after operating modifications with menuconfig | * Compare the old and new config files after operating modifications with menuconfig | ||
{{PC$}} make | '''Arm32bits''' {{PC$}}make ARCH=arm savedefconfig | ||
'''Arm64bits''' {{PC$}}make ARCH=arm64 savedefconfig | |||
Retrieve configuration updates by comparing the new defconfig and the old one | Retrieve configuration updates by comparing the new defconfig and the old one | ||
{{PC$}} meld defconfig defconfig.old | {{PC$}}meld defconfig defconfig.old | ||
* Cross-compile the Linux kernel (please check the load address in the ''README.HOW_TO.txt'' helper file) | * Cross-compile the Linux kernel (please check the load address in the ''README.HOW_TO.txt'' helper file) | ||
{{PC$}} make | For Arm32bits: | ||
{{PC$}} cp arch/arm/boot/uImage install_artifact/boot/ | '''Arm32bits''' {{PC$}}make ARCH=arm uImage LOADADDR=<loadaddr of kernel> | ||
'''Arm32bits''' {{PC$}}cp arch/arm/boot/uImage install_artifact/boot/ | |||
For Arm64bits: | |||
'''Arm64bits''' {{PC$}}make ARCH=arm64 Image.gz | |||
'''Arm64bits''' {{PC$}}cp arch/arm64/boot/Image.gz install_artifact/boot/ | |||
* Update the Linux kernel image on board | * Update the Linux kernel image on board | ||
{{PC$}} scp install_artifact/boot/uImage root@<board ip address>:/boot/ | '''Arm32bits''' {{PC$}}scp install_artifact/boot/uImage root@<board ip address>:/boot/ | ||
'''Arm64bits''' {{PC$}}scp install_artifact/boot/Image.gz root@<board ip address>:/boot/ | |||
* Reboot the board | * Reboot the board | ||
{{Board$}} cd /boot; sync; systemctl reboot | {{Board$}}cd /boot; sync; systemctl reboot | ||
Note that this use case modifies the configuration file in the Linux kernel build directory, not in the Linux kernel source directory: this is a temporary modification useful for a prototyping. | Note that this use case modifies the configuration file in the Linux kernel build directory, not in the Linux kernel source directory: this is a temporary modification useful for a prototyping. | ||
| Line 103: | Line 123: | ||
* Start the Linux kernel configuration menu | * Start the Linux kernel configuration menu | ||
{{PC$}} bitbake virtual/kernel -c menuconfig | {{PC$}}bitbake virtual/kernel -c menuconfig | ||
* Navigate forwards or backwards directly between feature | * Navigate forwards or backwards directly between feature | ||
| Line 115: | Line 135: | ||
* Cross-compile the Linux kernel | * Cross-compile the Linux kernel | ||
{{PC$}} bitbake virtual/kernel | {{PC$}}bitbake virtual/kernel | ||
* Update the Linux kernel image on board | * Update the Linux kernel image on board | ||
{{PC$}} scp <build dir>/tmp-glibc/deploy/images/<machine name>/uImage root@<board ip address>:/boot | For Arm32bits: | ||
{{PC$}}scp <build dir>/tmp-glibc/deploy/images/<machine name>/kernel/uImage root@<board ip address>:/boot | |||
For Arm64bits: | |||
{{PC$}}scp <build dir>/tmp-glibc/deploy/images/<machine name>/kernel/Image.gz root@<board ip address>:/boot | |||
{{Info|If the ''/boot'' mounting point does not exist yet, please see [[How to cross-compile with the Distribution Package#Creating a mounting point|how to create a mounting point]]}} | {{Info|If the ''/boot'' mounting point does not exist yet, please see [[How to cross-compile with the Distribution Package#Creating a mounting point|how to create a mounting point]]}} | ||
* if the new configuration made via '''menuconfig''' add or remove kernel modules, the kernel modules must be updated on board | |||
{{PC$}}scp <build dir>/tmp-glibc/deploy/images/<machine name>/kernel/modules-stripped-<kernel version>.tgz root@<board ip address>:/tmp | |||
{{Board$}}cd /lib/modules/$(uname -r); tar xf /tmp/modules-stripped-<kernel version>.tgz | |||
{{Board$}}depmod -a | |||
* Reboot the board | * Reboot the board | ||
{{Board$}} cd /boot; sync; systemctl reboot | {{Board$}}cd /boot; sync; systemctl reboot | ||
Note that this use case modifies the configuration file in the Linux kernel build directory, not in the Linux kernel source directory: this is a temporary modification useful for a prototyping. | Note that this use case modifies the configuration file in the Linux kernel build directory, not in the Linux kernel source directory: this is a temporary modification useful for a prototyping. | ||
Latest revision as of 11:40, 19 March 2025
1. Linux configuration genericity[edit | edit source]
The process of building a kernel has two parts: configuring the kernel options and building the source with those options.
The Linux® kernel configuration is found in the generated file: .config.
.config is the result of configuring task which is processing platform defconfig and fragment files if any.
For OpenSTLinux distribution the defconfig is located into the kernel source code and fragments into stm32mp BSP layer :
- - arch/arm/configs/multi_v7_defconfig for arm 32bits
- - arch/arm64/configs/defconfig for arm 64bits
Every new kernel version brings a bunch of new options, we do not want to back port them into a specific defconfig file each time the kernel releases, so we use the same defconfig file based on ARM SoC architecture.
STM32MP specificities are managed with fragments config files.
- - meta-st/meta-st-stm32mp/recipes-kernel/linux/linux-stm32mp/<kernel version>/fragment-*.config
.config result is located in the build folder:
- - build-openstlinuxweston-<machine name>/tmp-glibc/work/<machine>-ostl-linux-gnueabi/linux-stm32mp/<kernel recipe version>/build/.config
or config-<kernel-version> result is located in the deploy folder:
- - build-openstlinuxweston-<machine name>/tmp-glibc/deploy/image/<machine name>/kernel/config-<kernel recipe version>
To modify the kernel options, it is not recommended to edit this file directly.
- A user runs either a text-mode :
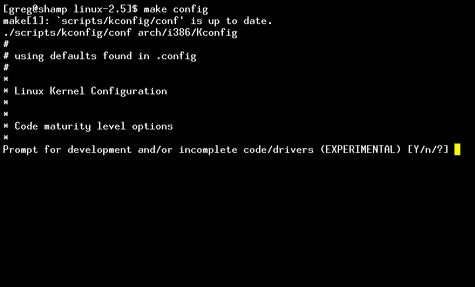
PC $>make config
starts a character based question and answer session (Figure 1)
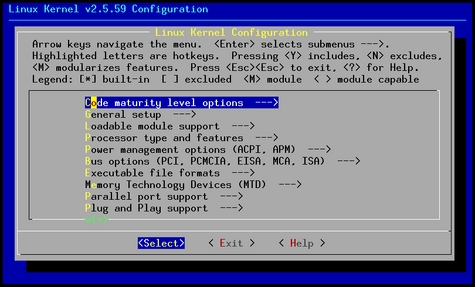
PC $>make menuconfig starts a terminal-oriented configuration tool (using ncurses) (Figure 2) The ncurses text version is more popular and is run with the make menuconfig option. Wikipedia Menuconfig[1] also explains how to "navigate" within the configuration menu, and highlights main key strokes.
- or a graphical kernel configurator :
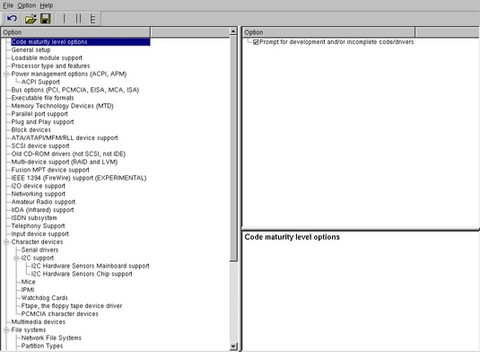
PC $>make xconfig
starts a X based configuration tool (Figure 3)
Ultimately these configuration tools edit the .config file.
An option indicates either some driver is built into the kernel ("=y") or will be built as a module ("=m") or is not selected.
The unselected state can either be indicated by a line starting with "#" (e.g. "# CONFIG_SCSI is not set") or by the absence of the relevant line from the .config file.
The 3 states of the main selection option for the SCSI subsystem (which actually selects the SCSI mid level driver) follow. Only one of these should appear in an actual .config file:
CONFIG_SCSI=y
CONFIG_SCSI=m
# CONFIG_SCSI is not set
2. Menuconfig and Developer Package[edit | edit source]
For this use case, the prerequesite is that OpenSTLinux SDK has been installed and configured.
To verify if your cross-compilation environment has been put in place correctly, run the following command:
For Arm32bits:
Arm32bits PC $>set | grep CROSS
CROSS_COMPILE=arm-ostl-linux-gnueabi-
For Arm64bits:
Arm64bits PC $>set | grep CROSS
CROSS_COMPILE=aarch64-ostl-linux-
For more details, refer to <Linux kernel installation directory>/README.HOW_TO.txt helper file (the latest version of this helper file is also available in GitHub: README.HOW_TO.txt ).
- Go to the <Linux kernel build directory>
PC $>cd <Linux kernel build directory>
- Save initial configuration (to identify later configuration updates)
Arm32bits PC $>make ARCH=arm savedefconfig
Arm64bits PC $>make ARCH=arm64 savedefconfig
Result is stored in defconfig file
PC $>cp defconfig defconfig.old
- Start the Linux kernel configuration menu
Arm32bits PC $>make ARCH=arm menuconfig
Arm64bits PC $>make ARCH=arm64 menuconfig
- Navigate forwards or backwards directly between feature
- un/select, modify feature(s) you want
- When the configuration is OK : exit and save the new configuration
useful keys to know:
enter: enter in config subdirectory
space: hit several times to either select [*], select in module [m] or unselect [ ]
/: to search for a keyword, this is usefull to navigate in tree
?: to have more information on selected line
- Compare the old and new config files after operating modifications with menuconfig
Arm32bits PC $>make ARCH=arm savedefconfig
Arm64bits PC $>make ARCH=arm64 savedefconfig
Retrieve configuration updates by comparing the new defconfig and the old one
PC $>meld defconfig defconfig.old
- Cross-compile the Linux kernel (please check the load address in the README.HOW_TO.txt helper file)
For Arm32bits:
Arm32bits PC $>make ARCH=arm uImage LOADADDR=<loadaddr of kernel>
Arm32bits PC $>cp arch/arm/boot/uImage install_artifact/boot/
For Arm64bits:
Arm64bits PC $>make ARCH=arm64 Image.gz
Arm64bits PC $>cp arch/arm64/boot/Image.gz install_artifact/boot/
- Update the Linux kernel image on board
Arm32bits PC $>scp install_artifact/boot/uImage root@<board ip address>:/boot/
Arm64bits PC $>scp install_artifact/boot/Image.gz root@<board ip address>:/boot/
- Reboot the board
Board $>cd /boot; sync; systemctl reboot
Note that this use case modifies the configuration file in the Linux kernel build directory, not in the Linux kernel source directory: this is a temporary modification useful for a prototyping.
- To make this temporary modification permanent, the delta between defconfig and defconfig.old must be saved in a configuration fragment file (fragment-*.config) based on fragment.cfg file, and the Linux kernel configuration/compilation steps must be re-executed (as explained in the README.HOW_TO.txt helper file).
3. Menuconfig and Distribution Package[edit | edit source]
- Start the Linux kernel configuration menu
PC $>bitbake virtual/kernel -c menuconfig
- Navigate forwards or backwards directly between feature
- un/select, modify feature(s) you want
- When the configuration is OK : exit and save the new configuration
useful keys to know:
enter: enter in config subdirectory
space: hit several times to either select [*], select in module [m] or unselect [ ]
/: to search for a keyword, this is usefull to navigate in tree
?: to have more information on selected line
- Cross-compile the Linux kernel
PC $>bitbake virtual/kernel
- Update the Linux kernel image on board
For Arm32bits:
PC $>scp <build dir>/tmp-glibc/deploy/images/<machine name>/kernel/uImage root@<board ip address>:/boot
For Arm64bits:
PC $>scp <build dir>/tmp-glibc/deploy/images/<machine name>/kernel/Image.gz root@<board ip address>:/boot
| If the /boot mounting point does not exist yet, please see how to create a mounting point |
- if the new configuration made via menuconfig add or remove kernel modules, the kernel modules must be updated on board
PC $>scp <build dir>/tmp-glibc/deploy/images/<machine name>/kernel/modules-stripped-<kernel version>.tgz root@<board ip address>:/tmp
Board $>cd /lib/modules/$(uname -r); tar xf /tmp/modules-stripped-<kernel version>.tgz
Board $>depmod -a
- Reboot the board
Board $>cd /boot; sync; systemctl reboot
Note that this use case modifies the configuration file in the Linux kernel build directory, not in the Linux kernel source directory: this is a temporary modification useful for a prototyping.
- To make this temporary modification permanent, it must be saved in a configuration fragment file (fragment-*.config) based on fragment.cfg file, and the Linux kernel configuration/compilation steps must be re-executed: bitbake <name of kernel recipe>.
4. References[edit | edit source]